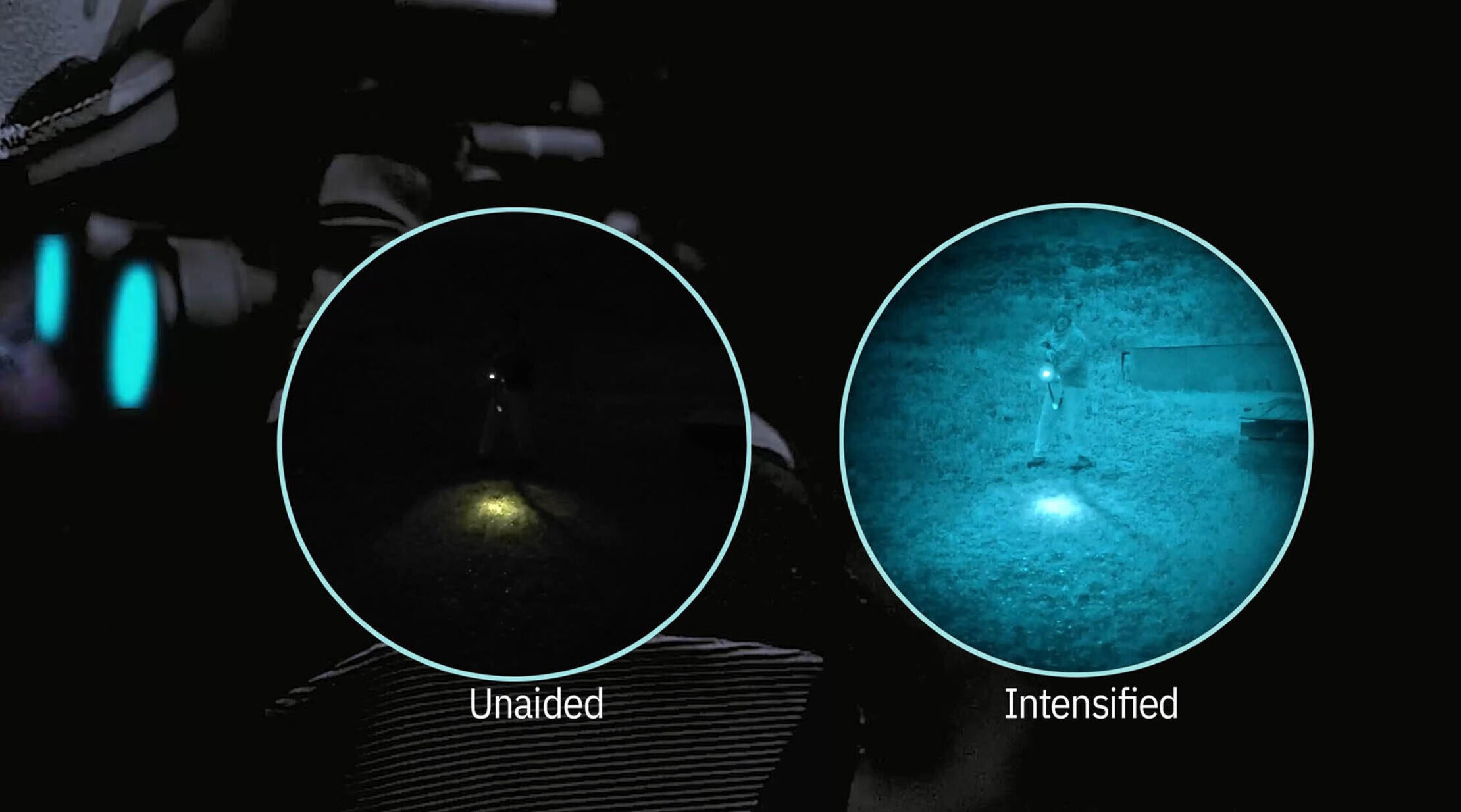
Night vision systems with advanced image intensifier tube technology delivers amplified visibility in low-light environments so troops can see targets first and engage them before being seen.
Night vision technology has also advanced significantly over the years, including enhanced image quality, sensitivity and overall performance to keep up with emerging challenges they face on the battlefield.
“Much of the night vision system’s performance a user receives depends on the type – and quality – of the tube technology it leverages,” said Sven Rowley, Account Management Director, L3Harris Technologies. “The challenge for defense organizations today is that there are few meaningful industry-wide testing standards that objectively evaluate tubes against each other with quantitative data about important characteristics.”
A History of Innovation

Image intensifier technology began to emerge before World War II, but the first “generation” (Gen I) tube wasn’t invented until the 1960s. Since then, technology improvements have led to the introduction of several generations of image intensifier tubes, based on U.S. military definitions.
Gen II tubes emerged in the late 1970s and expanded mission options while increasing tube resolution and lifespan through improved photocathodes and introducing microchannel plates. Gen III tubes, now widely used in western militaries with enhanced sensitivity for tactical operations, introduced a gallium arsenide photocathode and an ion barrier to the microchannel plates in the 1980s, dramatically increasing resolution, brightness and lifespan.
“As the Trusted Disruptor in the defense industry, L3Harris Technologies goes a step further than competitors to deliver an unfilmed Gen III tube to provide exceptional resolution, even in low light, and a longer lifespan,” said Jon Burnsed, Senior Systems Engineering Scientist, L3Harris. “The removal of the ion barrier and inclusion of auto-gating to manage bright light conditions facilitates higher-end tactical mission sets.”
As there is no military specification to define a “Gen IV” designation, such a tube generation does not currently exist, added Rowley.